Spring Bean的生命周期
生命周期
普通的Java程序中一个对象通过关键字new进行实例化, 而在Spring容器里, Bean的生命周期由Spring来控制, 而Spring中对Bean的生命周期的控制非常细致, 我们可以通过Spring提供的扩展点来自定义Bean的创建过程.
下图是一个典型的生命周期过程:
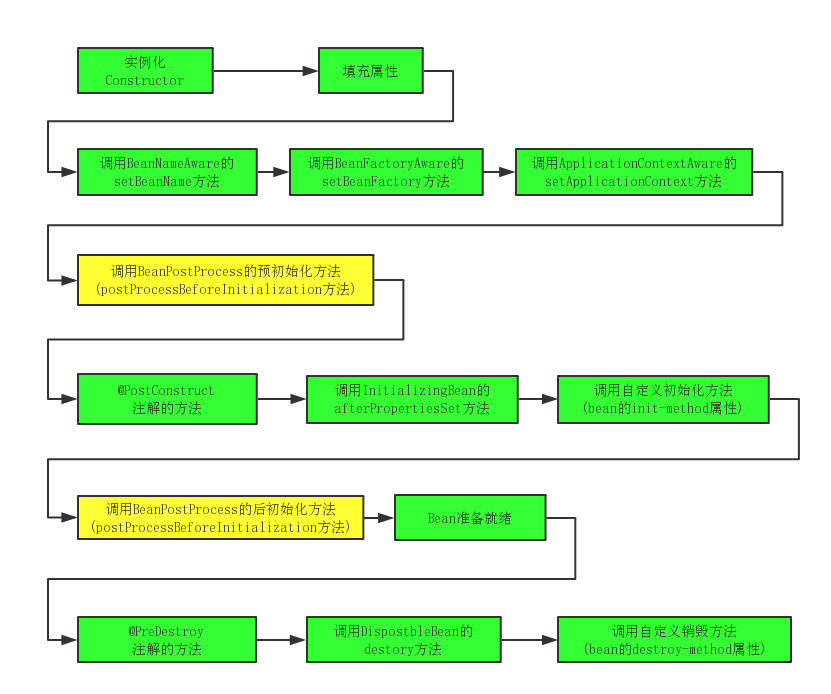
- 对
Bean进行实例化, 相当于调用构造函数,new出一个对象 - 将
值和Bean的引用注入到Bean对应的属性中 - 若
Bean实现了BeanNameAware接口, Spring将Bean的ID传递给setBeanName(String name)方法. (实现BeanNameAware主要是为了通过Bean的引用来 获取 Bean的ID) - 若
Bean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口, Spring将调用setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory)方法, 将BeanFactory容器实例传入. (实现BeanFactoryAware主要目的是为了获取Spring容器, 如Bean通过Spring容器发布事件等) - 若
Bean实现了ApplicationContextAware接口, Spring容器将调用setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext)方法, 将应用上下文的引用传入. (作用与BeanFactoryAware类似都是为了获取Spring容器, 不同的是Spring容器在调用setApplicationContext方法时会把自己作为参数传入, 而Spring容器在调用setBeanFactory前需要程序员自己指定setBeanFactory里的参数BeanFactory) - 若
Bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口, Spring将调用它们的预初始化方法: postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)方法. (作用是在Bean实例创建成功后对进行增强处理, 如对Bean进行修改, 增加某个功能) - 调用
@PostConstruct注解的方法, 该方法必须无参数, 不能抛受检查异常, 返回值必须为void. - 若
Bean实现了InitializingBean接口, Spring将调用它们的afterPropertiesSet()方法. - 调用自定义初始化方法, 即
<bean init-method="" />或@Bean(initMethod = "")声明的方法. - 若
Bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类, Spring将调用它们的后初始化方法: postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)方法. - 此时
Bean已经准备就绪, 可以被应用程序使用了, 它将一直驻留在应用上下文中, 直到应用上下文被销毁 - 调用
@PreDestroy注解的方法, 该方法必须无参数, 不能抛受检查异常, 返回值必须为void. - 若
Bean实现了DisposableBean接口, Spring将调用它的destroy()方法. - 调用自定义销毁方法, 即
<bean destroy-method="" />或@Bean(destroyMethod = "")声明的方法.
注意: 黄色部分标识的BeanPostProcessor接口有点特殊, 如果我们定义了一个实现BeanPostProcessor接口的Bean(后处理器), 那么在这个Bean所在的容器中的 其他所有Bean 在初始化前后都会执行该后处理器的方法
测试示例
如果我们在xml文件中有这样的配置
<bean id="lifecycleService" class="XXX.service.LifecycleService"
init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod"/>
Bean的定义如下:
// 后处理器
@Service
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LifecycleService.class);
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 每一个没有实现BeanPostProcessor接口的Bean都会调用
if (bean instanceof LifecycleService) {
logger.info("BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法, beanName={}", beanName);
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 每一个没有实现BeanPostProcessor接口的Bean都会调用
if (bean instanceof LifecycleService) {
logger.info("BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法, beanName={}", beanName);
}
return bean;
}
}
// 一个普通的Bean, 在上面的xml文件中声明
public class LifecycleService implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LifecycleService.class);
public LifecycleService() {
logger.info("1. 构造方法");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String beanName) {
logger.info("2. BeanNameAware.setBeanName()方法, 用于获取Bean的ID");
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
logger.info("3. BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()方法");
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
logger.info("4. ApplicationContextAware.setApplicationContext()方法");
}
@PostConstruct
private void init() {
logger.info("5. @PostConstruct");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
logger.info("6. InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()方法");
}
public void initMethod() {
logger.info("7. initMethod");
}
// bean就绪
@PreDestroy
public void preDestory() {
logger.info("8. @PreDestroy");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
logger.info("9. DisposableBean.destroy()方法");
}
public void destroyMethod() throws Exception {
logger.info("10. destroyMethod");
}
}
这个例子的输出结果为:
1. 构造方法
2. BeanNameAware.setBeanName()方法, 用于获取Bean的ID
3. BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()方法
4. ApplicationContextAware.setApplicationContext()方法
BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法, beanName=lifecycleService
5. @PostConstruct
6. InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()方法
7. initMethod
BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法, beanName=lifecycleService
8. @PreDestroy
9. DisposableBean.destroy()方法
10. destroyMethod